
Django Tutorial
Installation & Setup
Let's start by installing Django and create our project. For this tutorial we will be using PyCharm. You can install the community edition for free. Once installed open a terminal in pycharm:
- First install Django:
- Add the app to settings.py
- We will be using a folder structure to separate files for easier management:
- Enable Templates & Static files in settings.py:
- Add allowed Hosts to settings.py:
- Create security settings in setting.py (at the end of the file after the last line:
- Add CSRF Tokens:
- Create Views for pages in views.py
- Create a file called urls.py and add URLs to it (use namespace if you plan on adding more apps later):
- Create database migrations
# Install Django
pip install django
# Create project
django-admin startproject daemons_code_library
cd daemons_code_library
# Create app
python manage.py startapp code_library
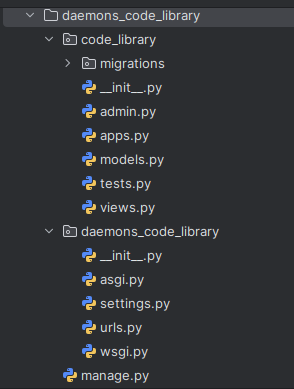
The folder structure should now look like this:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'code_library', <-- add this
]
cd code_library
mkdir templates static
mkdir static/css static/js static/images
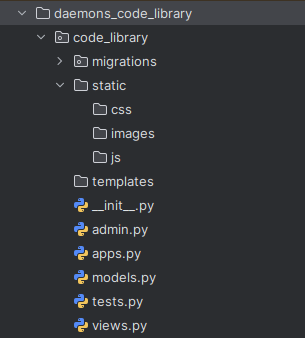
The folder structure should now look like this:
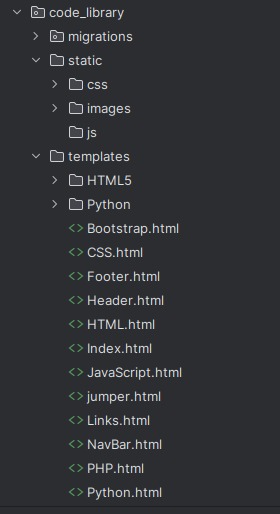
Move the files as follows: • HTML/PHP files (like index.php, header.php, footer.php, HTML.php, etc.) → code_library/templates/ • Style.css → code_library/static/css/Style.css • Script.js → code_library/static/js/Script.js • Images → code_library/static/images/ • Other folders (HTML5, CSS, PHP, Django, Javascript) → code_library/templates/html5/basics1.html ect.
The folder structure should now look like this:
import os <-- add this
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
# Templates
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [BASE_DIR / "code_library" / "templates"], <-- add this
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
# Static files
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = [BASE_DIR / "code_library" / "static"] <-- add this
find ALLOWED_HOSTS = [}
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ["yourdomain", "127.0.0.1", "localhost"] <-- add this
# ==============================
# Django Security Settings
# ==============================
# Use HTTPS everywhere
SECURE_SSL_REDIRECT = True # Redirect all HTTP → HTTPS
SECURE_HSTS_SECONDS = 31536000 # 1 year (adjust if testing)
SECURE_HSTS_INCLUDE_SUBDOMAINS = True
SECURE_HSTS_PRELOAD = True
# Protect against content sniffing
SECURE_CONTENT_TYPE_NOSNIFF = True
# Prevent XSS
SECURE_BROWSER_XSS_FILTER = True # Some browsers (older)
X_FRAME_OPTIONS = "DENY" # Prevent clickjacking (use "SAMEORIGIN" if you need iframes)
# CSRF Protection
CSRF_COOKIE_SECURE = True
CSRF_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True
# Session / Cookie Security
SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = True
SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True
SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = True
# Referrer Policy (optional, but good practice)
SECURE_REFERRER_POLICY = "strict-origin-when-cross-origin"
find CSRF_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True and below it insert this line:
CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGINS = ["https://yourdomain", "https://127.0.0.1", "localhost"] <-- add this
from django.shortcuts import render
def index(request):
return render(request, "index.html")
def html_page(request):
return render(request, "HTML.html")
def css_page(request):
return render(request, "CSS.html")
def php_page(request):
return render(request, "PHP.html")
def python_page(request):
return render(request, "Python.html")
from django.urls import path
from . import views
app_name = "code_library" # 👈 namespace for this app
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name="home"),
path('html/', views.html_page, name="html"),
path('css/', views.css_page, name="css"),
path('php/', views.php_page, name="php"),
path('python/', views.python_page, name="python"),
]
In daemons_code_library/urls.py, add the following:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include <-- add 'include' to this line
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include('code_library.urls', namespace="code_library")), <-- add this
]
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
This is the basic setup to get Django running. Only thing left to do is run the server:
python manage.py runserver
You can now access your page on: http://127.0.0.1:8000 or http://localhost:8000
Simple Admin Panel:
Django has a simple admin panel built-in to create users ect. We will create a simple e-commerce panel:
Follow above steps and create the following:
- project: ecommerce_admin
- app: products
- add app to settings.py
- Create the Product model in products/models.py
- Create Register Product in admin.py
- Create CRUD Views in products/views.py
- Create Product Form in products/forms.py
- Set Up URLs in ecommerce_admin/urls.py
- Create a templates folder inside your app and add:
- templates/products/product_list.html
- templates/products/product_form.html
- templates/products/product_confirm_delete.html
- templates/login.html
- Create database migrations
- Create superuser
from django.db import models
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=200)
description = models.TextField(blank=True)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2)
stock = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Product
@admin.register(Product)
class ProductAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = ('name', 'price', 'stock', 'created_at')
search_fields = ('name',)
list_filter = ('created_at',)
ordering = ('-created_at',)
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, get_object_or_404
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
from .models import Product
from .forms import ProductForm
@login_required
def product_list(request):
products = Product.objects.all()
return render(request, 'products/product_list.html', {'products': products})
@login_required
def product_create(request):
if request.method == "POST":
form = ProductForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return redirect('product_list')
else:
form = ProductForm()
return render(request, 'products/product_form.html', {'form': form})
@login_required
def product_update(request, pk):
product = get_object_or_404(Product, pk=pk)
if request.method == "POST":
form = ProductForm(request.POST, instance=product)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return redirect('product_list')
else:
form = ProductForm(instance=product)
return render(request, 'products/product_form.html', {'form': form})
@login_required
def product_delete(request, pk):
product = get_object_or_404(Product, pk=pk)
if request.method == "POST":
product.delete()
return redirect('product_list')
return render(request, 'products/product_confirm_delete.html', {'product': product})
from django import forms
from .models import Product
class ProductForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Product
fields = ['name', 'description', 'price', 'stock']
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from products import views as product_views
from django.contrib.auth import views as auth_views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(template_name='login.html'), name='login'),
path('logout/', auth_views.LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout'),
path('', product_views.product_list, name='product_list'),
path('create/', product_views.product_create, name='product_create'),
path('update/<int:pk>/', product_views.product_update, name='product_update'),
path('delete/<int:pk>/', product_views.product_delete, name='product_delete'),
]
<h1>Products</h1>
<a href="{% url 'product_create' %}">Add Product</a>
<a href="{% url 'logout' %}">Logout</a>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name
</th>
<th>Price
</th><th>Stock
</th>
<th>Actions
</th>
</tr>
{% for product in products %}
<tr>
<td>{{ product.name }}</td>
<td>${{ product.price }}</td>
<td>{{ product.stock }}</td>
<td>
<a href="{% url 'product_update' product.pk %}">Edit</a>
<a href="{% url 'product_delete' product.pk %}">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
<h1>{{ form.instance.pk|yesno:"Edit Product,Add Product" }}</h1>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</form>
<a href="{% url 'product_list' %}">Back</a>
<h1>Delete Product</h1>
<p>Are you sure you want to delete "{{ product.name }}"?</p>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<button type="submit">Yes, delete</button>
</form>
<a href="{% url 'product_list' %}">Cancel</a>
<h1>Login</h1>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form>
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
Just follow the prompts for username, email (if required) and password
Now you have a fully functional admin panel.
You can now access your panel on: http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin or http://localhost:8000/admin
To login, use the credentials you created earlier.
Django Quickstart Script
Here is a simple script to install Django and create a simple website:
Django Quickstart